Information on this page was collected from the source acknowledged below:
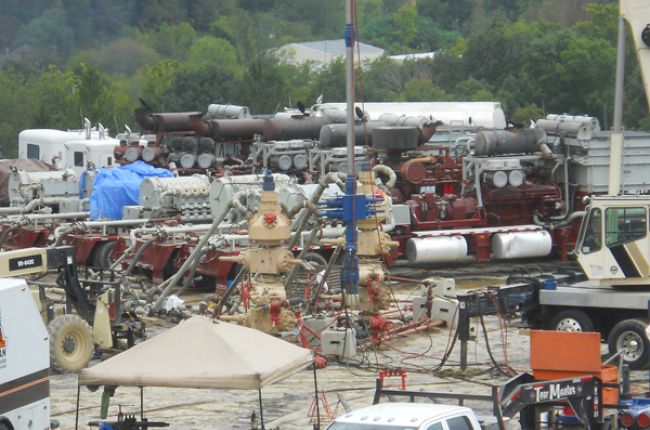
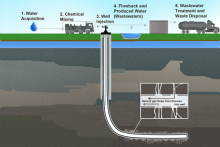
"The actual practice of hydraulic fracturing (or “fracking”) is only a small part of the overall process of drilling, completing, and producing an oil and gas well. Environmental issues that are specifically related to hydraulic fracturing include:
- water availability
- spills of chemicals at the surface
- impacts of sand mining for use in the hydraulic fracturing process
- surface water quality degradation from waste fluid disposal
- groundwater quality degradation
- induced seismicity from the injection of waste fluids into deep disposal wells
Any kind of oil and gas drilling can additionally cause:
- reduced air quality
- noise
- night sky light pollution
- landscape changes such as forest fragmentation
- disruption to wildlife corridors and habitats
It is important to note that not all of these potential impacts occur at every site and many impacts can be avoided or mitigated with the proper practices."
Learn More:
- Critical Issue: Hydraulic Fracturing (Webpage and Issue Brief), Geological Society of America
This peer-reviewed report provides a thoroughly researched overview of hydraulic fracturing ("fracking"). Defines hydraulic fracturing, discusses its role in energy development, and addresses potential environmental issues associated with the use of the technology.
- Assessment of the Potential Impacts of Hydraulic Fracturing for Oil and Gas on Drinking Water Resources (Report), U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
2015 report assessing the potential for hydraulic fracturing to affect drinking water resources.
- Unconventional Oil and Natural Gas Development (Webpage), U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
Overview of hydraulic fracturing as a method of extracting oil and natural gas, including the regulatory framework surrounding hydraulic fracturing; wastewater treatment and disposal; and air quality impacts.