By the numbers: Oklahoma
- 8,200 geoscience employees (excludes self-employed)1
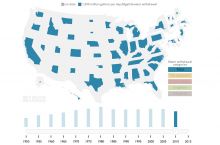
- 1.11 billion gallons/day: total groundwater withdrawal3
- $700 million: value of nonfuel mineral production in 20174
- 167 total disaster declarations, including 84 fire, 39 severe storm, and 22 flood disasters (1953-2017)6
- $2.94 million: NSF GEO grants awarded in...
Agencies Working on Geoscience Issues in oklahoma
The Oklahoma Department of Emergency Management (OEM) prepares for, responds to, recovers from and mitigates against disasters and emergencies. The department maintains the State Emergency Operations Center which serves as a command center for reporting emergencies and coordinating state response activities. OEM delivers service to Oklahoma cities, towns and counties through the network of more than 400 local emergency managers.
The mission of the Oklahoma Department of Environmental Quality is to enhance the quality of life in Oklahoma and protect the health of its citizens by protecting, preserving and restoring the water, land and air of the state, thus fostering a clean, attractive, healthy, prosperous and sustainable environment.
The Oklahoma Geological Survey is charged with investigating the state's land, water, mineral, and energy resources and disseminating the results of those investigations to promote the wise use of Oklahoma's natural resources consistent with sound environmental practices.
The mission of the OWRB is to protect and enhance the quality of life for Oklahomans by managing and improving the state’s water resources to ensure clean and reliable water supplies, a strong economy, and a safe and healthy environment.