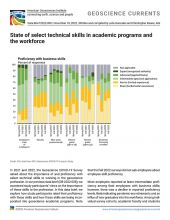
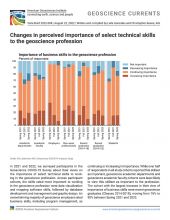
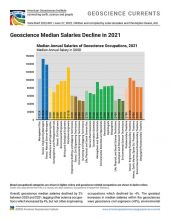
Financial Performance
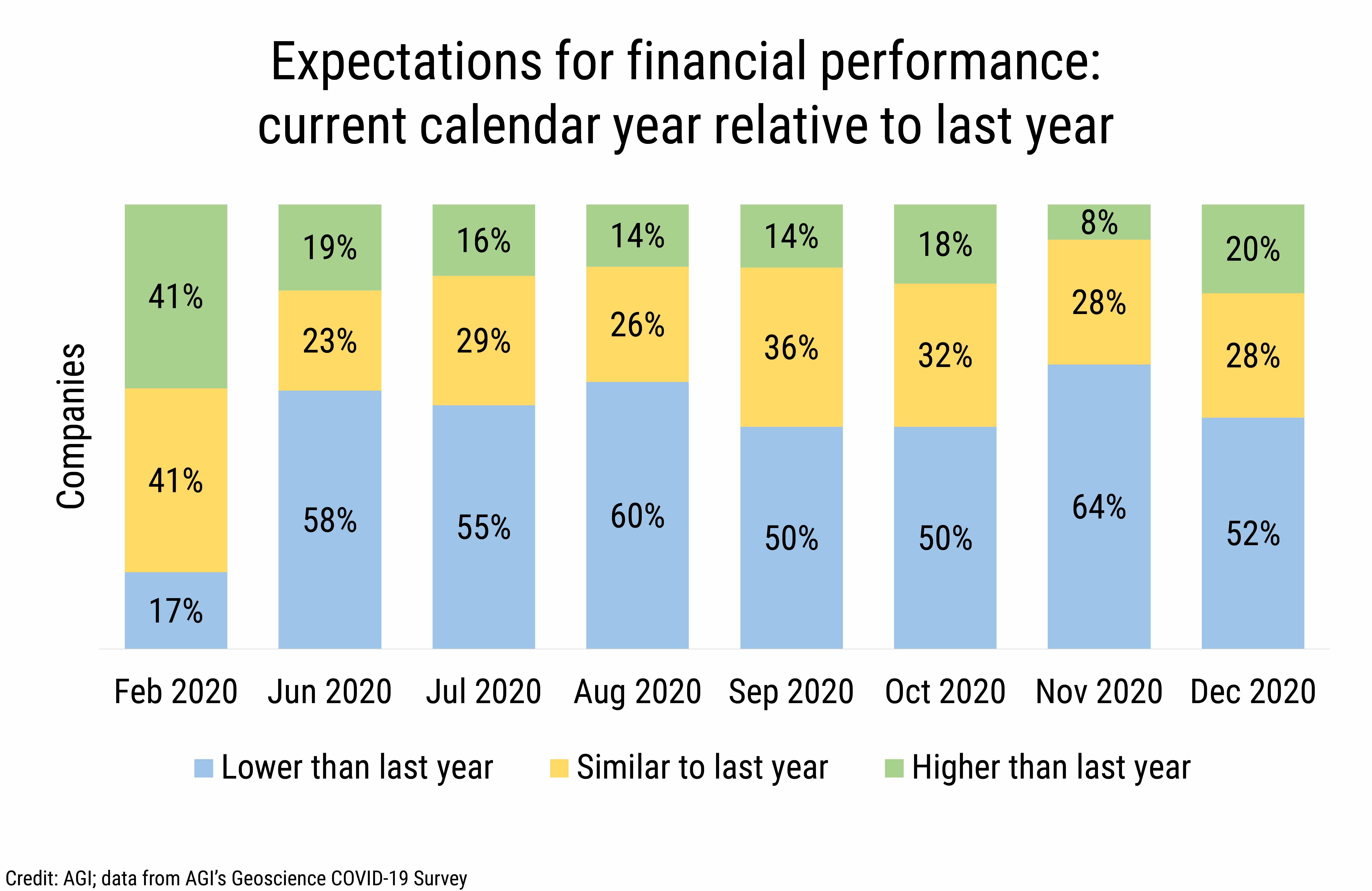
From June through December 2020 between 50% and 64% of geoscience employers reported expectations of lower financial performance relative to 2019. Over the same period, the percentage of companies reporting either similar or better financial performance relative to 2019 varied between a high of 50% in September and October and a low of 36% in November. By December, expectations of financial performance were nearly split in half with 48% of companies reporting similar or better financial performance relative to 2019 and 52% reporting expectations of lower financial performance.
Productivity
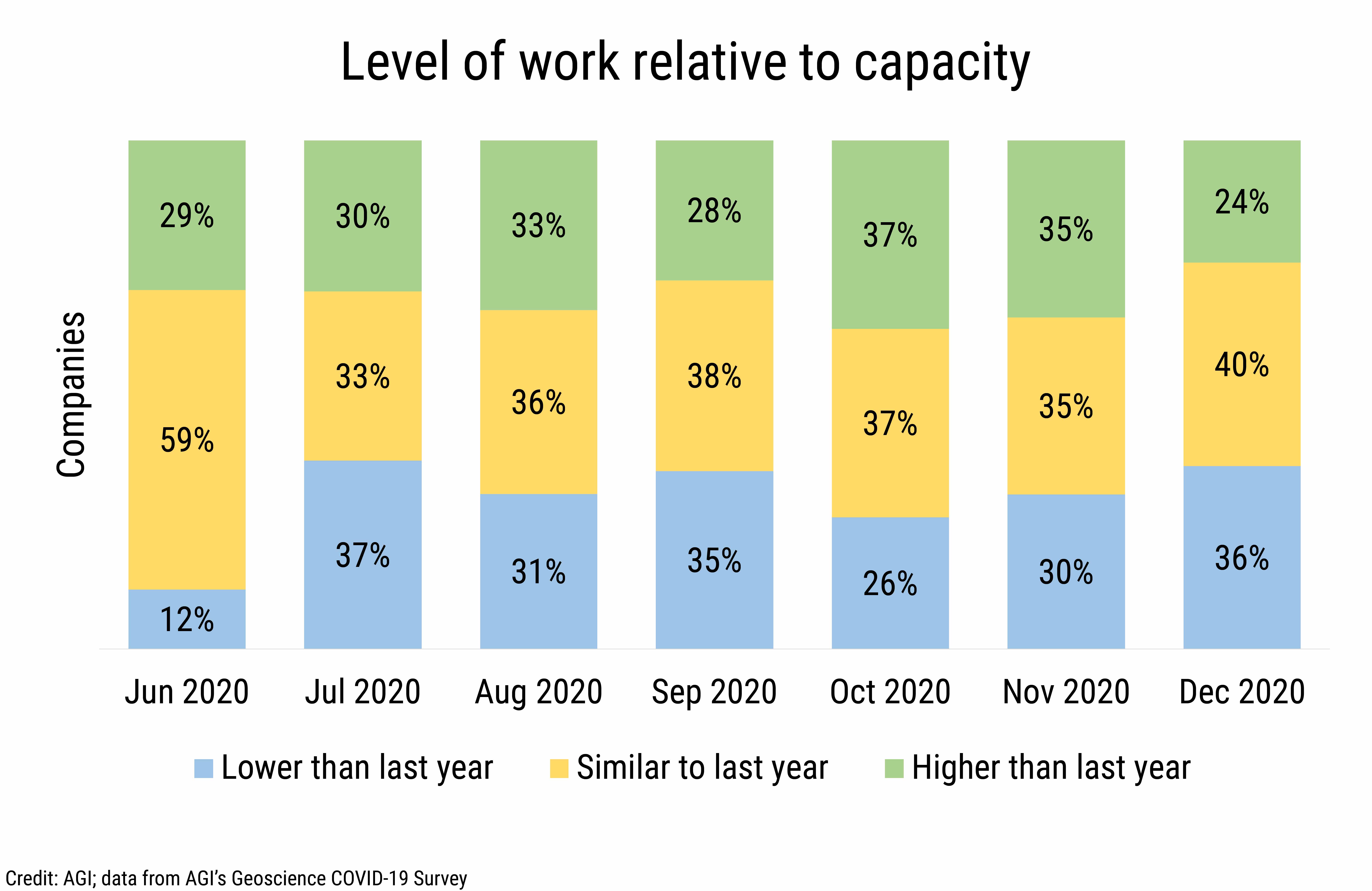
Throughout the summer and fall of 2020, approximately 30% of companies reported increased workloads relative to staffing, with increased workloads peaking in October at 37%, thereafter declining to 24% by the end of the year. Meanwhile, the percentage of companies reporting decreased workloads relative to staffing fluctuated between 30% and 37%, with the exception of October, when productivity increased and only 26% of companies reported decreased workloads relative to staffing.
Financial Assistance
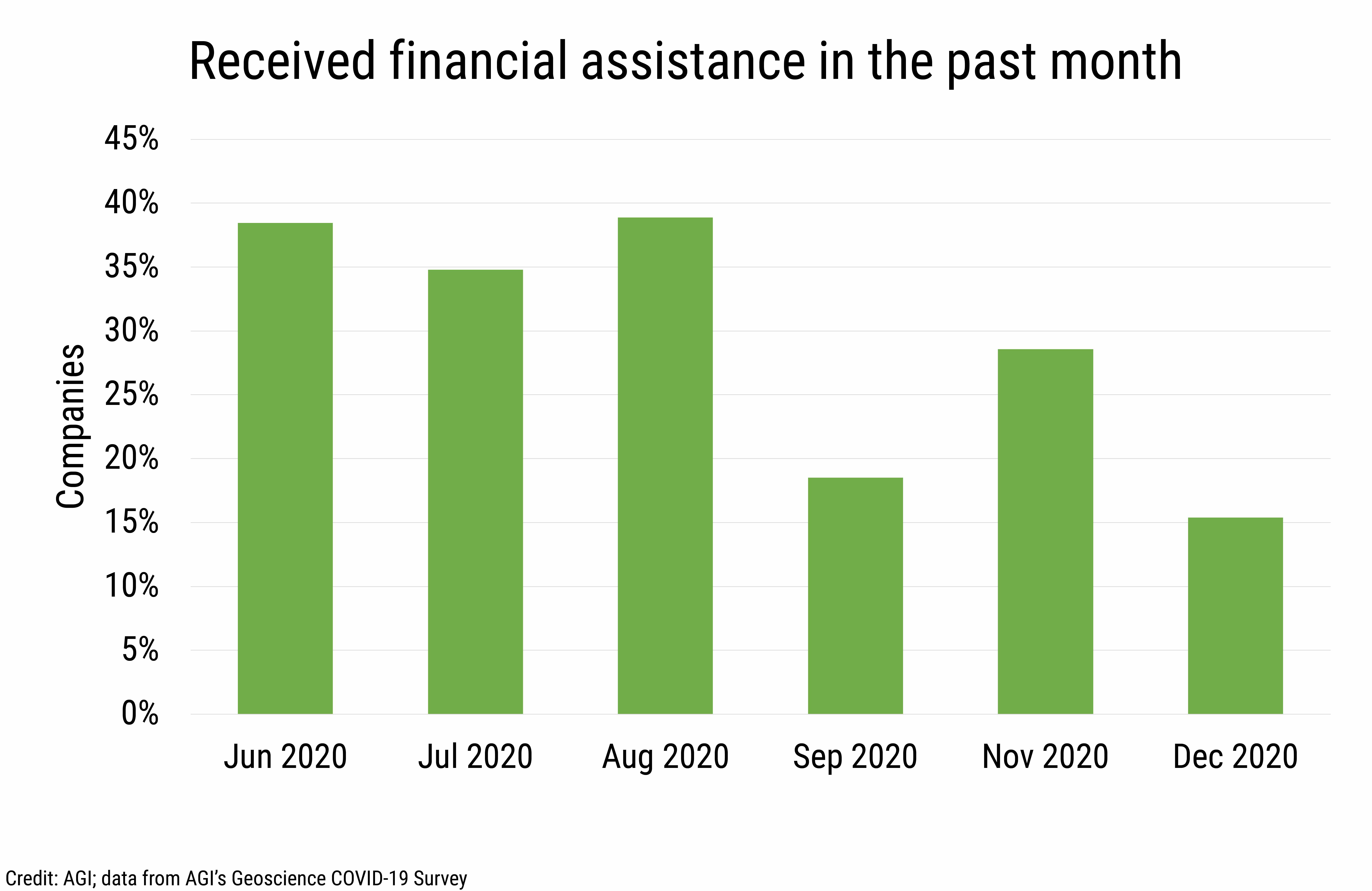
During the summer of 2020, just over one-third of companies reported receiving financial assistance, and this percentage dropped to 19% in September and further declined to 15% in December.
Business Impacts
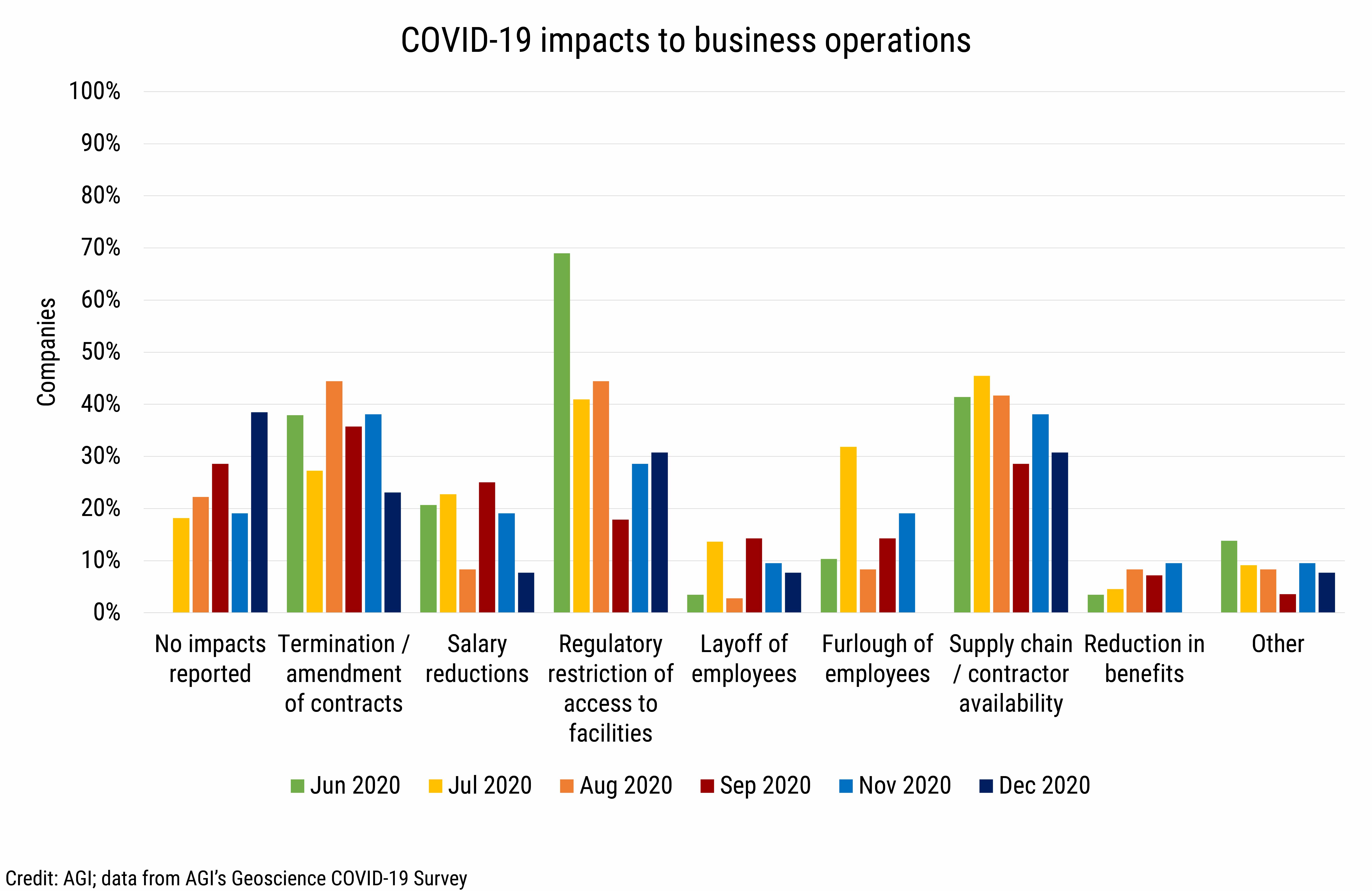
The most common COVID-19 impact to business operations in 2020 was regulatory restriction of access to facilities which impacted just over two-thirds of businesses in June 2020 and was an issue for over 40% of businesses through the rest of the summer months. Supply chain disruptions and issues with contractor availability were reported by over 40% of businesses through the summer of 2020, and termination or amendment of revenue-generating contracts impacted between 23% and 44% of companies in 2020. In terms of impacts to staff, salary reductions were more commonly reported (21-25%) than staff furloughs (8-32%) or layoffs (3-14%), although in July, staff furloughs were the most common staffing impact, affecting nearly one-third of businesses. Throughout 2020, the percentage of businesses reporting no impacts increased from 18% in July to 38% in December.
Office Space Usage and Supply Shortages
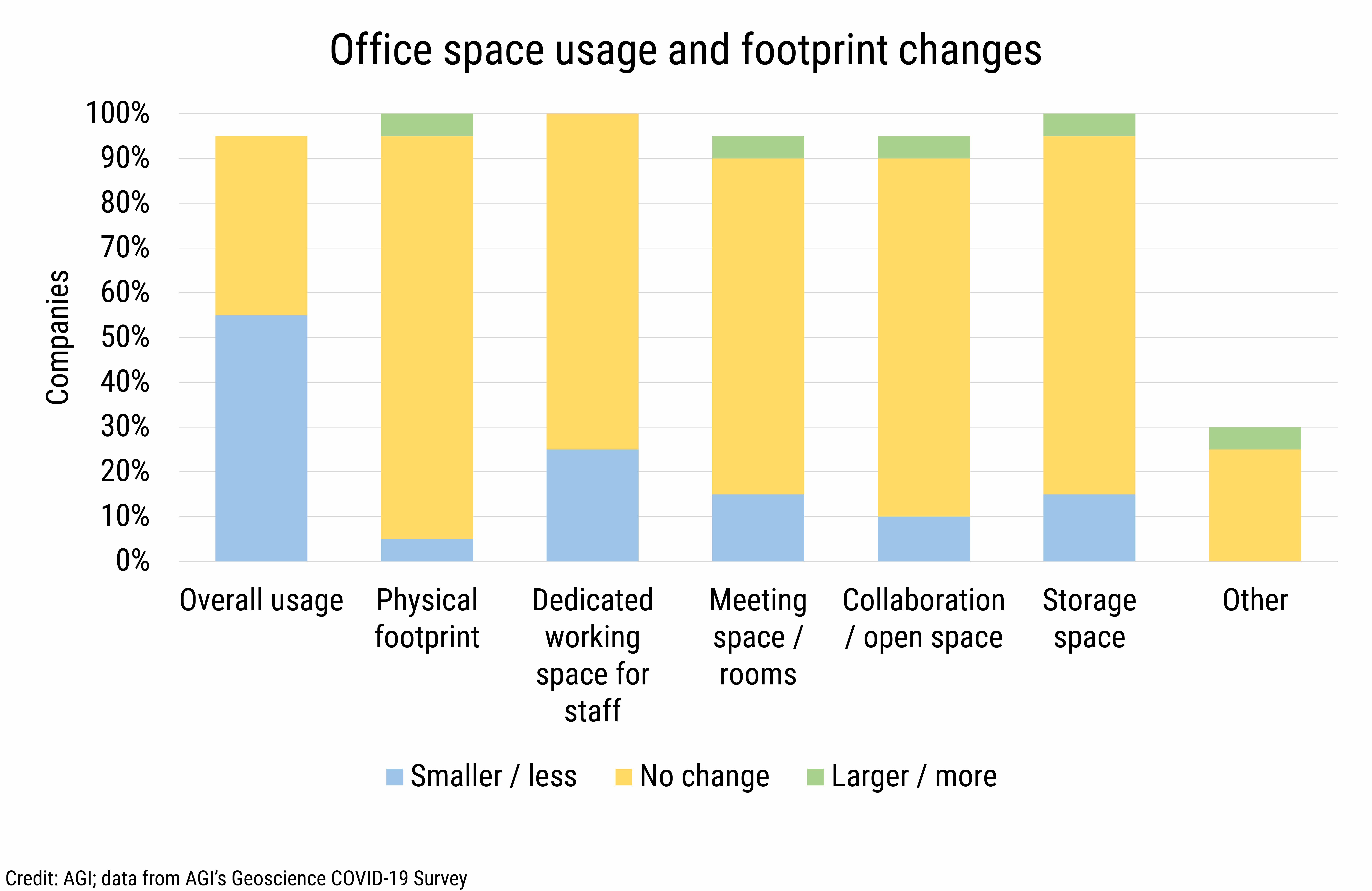
With employers suggesting a possible shift towards permanent telework and limited in-office attendance, we asked in our November 2020 surveys about how the usage of office space has changed since March 2020. While the overall usage of office space declined for just over half of employers, most employers reported no change in the physical footprint or usage of specific office areas (i.e., dedicated working space for staff, meeting rooms, open space, storage space, etc.).
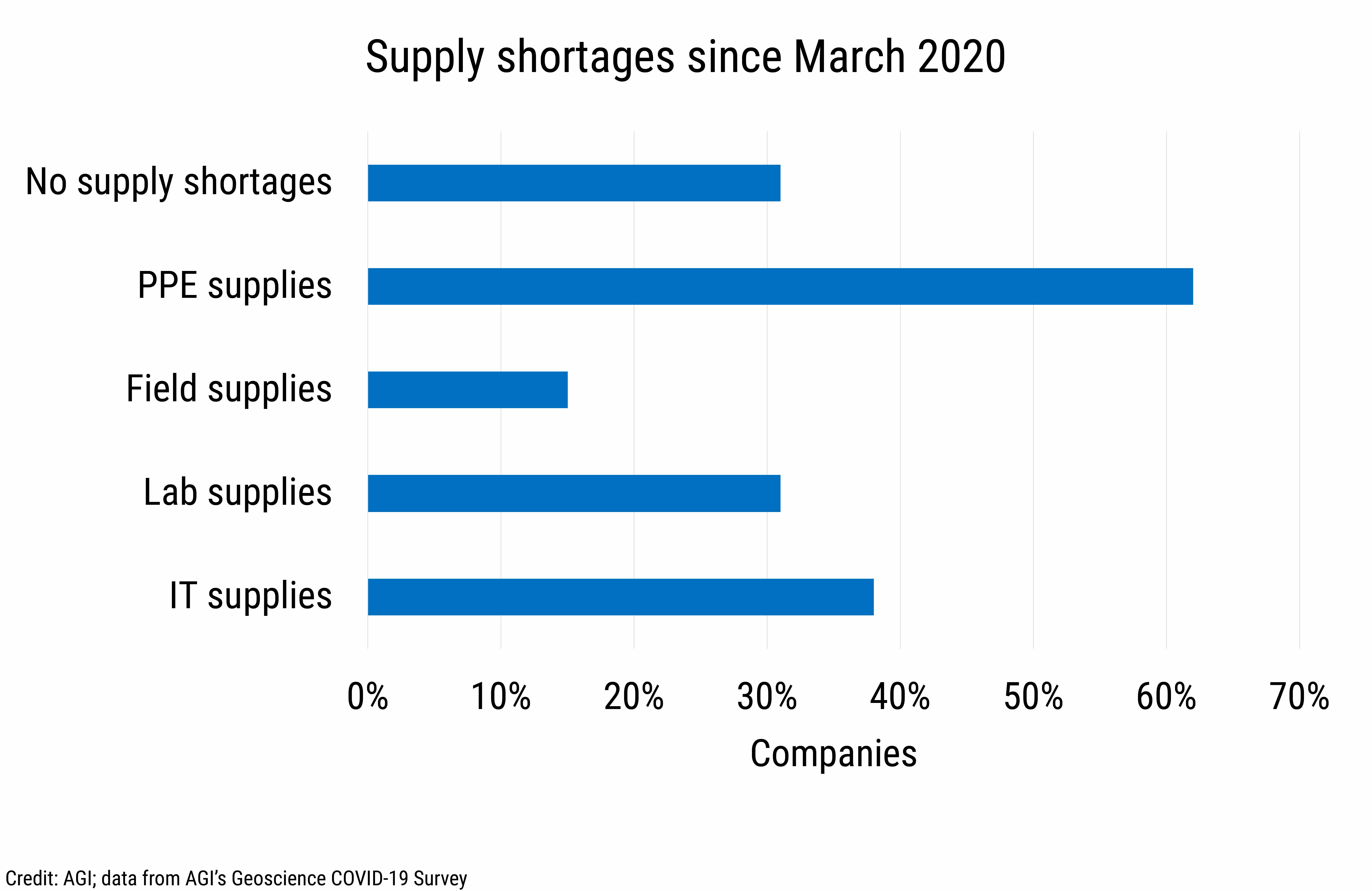
In December 2020, we asked about supply shortages since the start of the pandemic. While nearly one-third of employers reported no supply shortages, 62% of employers reported supply shortages related to personal protective equipment (PPE), 38% reported shortages related to technology equipment, and nearly one-third of employers reported shortages related to lab supplies.
Strategies, Concerns, and Opportunities
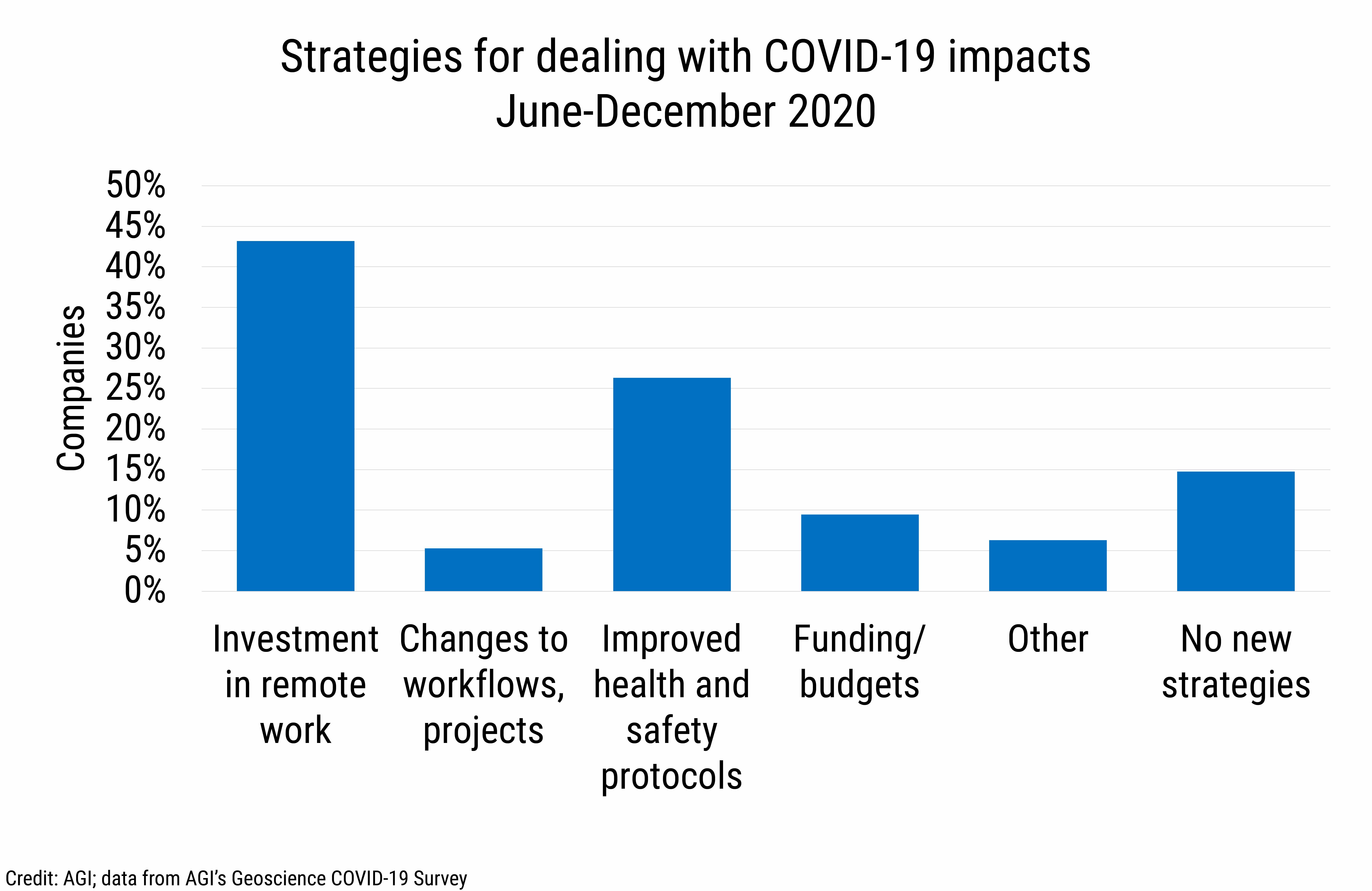
Geoscience employers dealt with COVID-19 impacts in 2020 predominantly by investing in remote work technologies followed by implementation of health and safety protocols for those working in facilities, offices, and at field sites. Furthermore, 41% of companies indicated that they were considered "essential" by state or local government regulations.
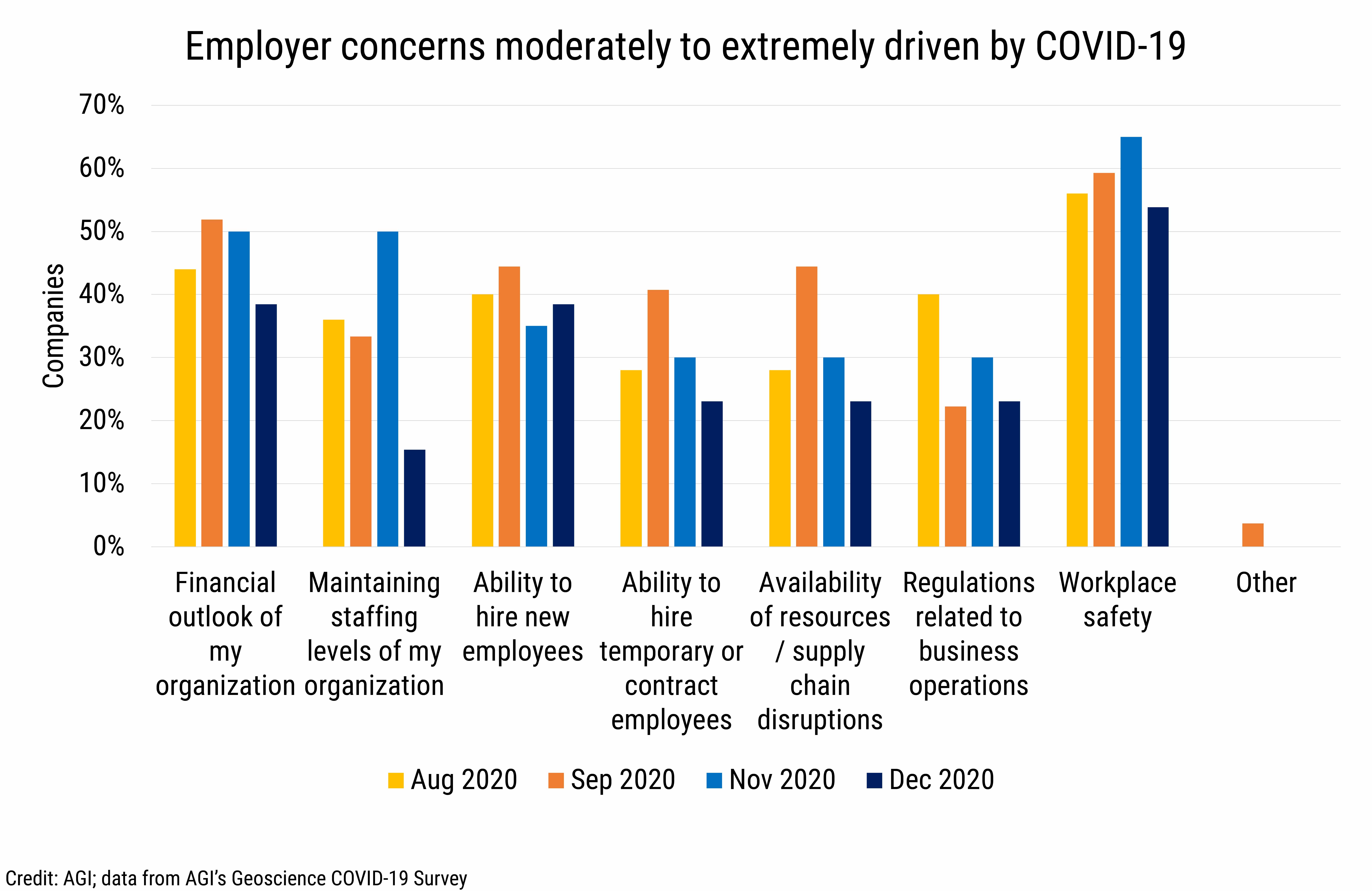
The top reported pandemic-related employer concerns in 2020 were workplace safety and financial outlook of companies. In September 2020, over 40% of businesses reported among their top concerns hiring permanent and temporary workers and supply chain disruptions. Additionally, in November, half of businesses reported among their top concerns maintaining staffing levels.
In December, we asked about new opportunities and changes in the focus/topics of projects and research due to the pandemic. For most businesses (77%), the pandemic did not provide opportunities to explore new areas of research or work. Furthermore, 83% of businesses reported that they had not changed the focus or topics of projects and research due to COVID-19.
We will continue to provide current snapshots on the impacts of COVID-19 on the geoscience enterprise throughout the year. For more information, and to participate in the study, please visit: www.americangeosciences.org/workforce/covid19
Funding for this project is provided by the National Science Foundation (Award #2029570). The results and interpretation of the survey are the views of the American Geosciences Institute and not those of the National Science Foundation.