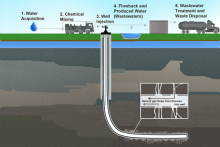
"Most of the water and additives used in hydraulic fracturing (or “fracking”) remain deep underground in the geologic formation from which the oil or gas is being extracted. But some of the fluid, mixed with water or brine from the formation, returns through the well to the surface and is referred to as “produced water”. After a well is brought on-line, large volumes of produced water (primarily composed of the injected fluid) are generated.
Produced water is often disposed of by injecting it into deep geologic formations via wells that are specifically designed for that purpose. In some cases, produced water can be treated and reused to hydraulically fracture another well. In other cases, the water is clean enough to meet regulatory standards and is discharged into local watersheds. Practices vary between regions, depending on regulations, geologic conditions, and water availability."
For additional information on injection wells, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s Underground Injection Control Website provides information on Class II wells and how they protect water resources. Additionally, there is more information about the potential for waste water injection to induce earthquakes in a U.S. Geological Survey Science Feature, these Frequently Asked Questions, and two AGI webinars from 2015 and 2017.
Learn More
- Flowback and Produced Waters: Opportunities and Challenges for Innovation (Report), National Academy of Sciences
Summary of a 2016 workshop on the reuse, disposal, and treatment of produced and flowback water from hydraulic fracturing and other oil and gas operations
- The Hydraulic Fracturing Water Cycle (Webpage), Environmental Protection Agency
Basic overview of the use of water in the process of hydraulic fracturing.
- Basic Information about Underground Injection Wells (Webpage), Environmental Protection Agency
Describes an injection well, what they are used for, how they are categorized, how EPA regulations protect ground water, and links to contact information.
- Earthquakes Induced by Fluid Injection (FAQ), U.S. Geological Survey
After filtering for "Earthquakes Induced by Fluid Injection," answers to several questions relevant to induced seismicity.
- Making Produced Water More Productive (Webinar), American Geosciences Institute
2015 webinar addressing the scientific and regulatory background of produced water, how it is disposed, potential options for reuse, and the environmental and regulatory challenges that influence reuse and disposal.
- State Responses to Induced Earthquakes (Webinar), American Geosciences Institute
2017 webinar on how Oklahoma, Texas, and Ohio have responded to induced earthquakes on the state level. Includes a lot of information on how and where produced and flowback waters are disposed, as well as information on regulations in each state surrounding the disposal of wastewater from oil and gas operations.