Weather hazards impact the entire country, with enormous effects on the economy and public safety. Since 1980, weather/climate disasters have cost the U.S. economy more than $1.5 trillion. In an average year, the United States will be affected by six billion-dollar weather/climate disasters, but this number has increased in recent years: from 2013-2017 the average was 11.6 events.
Basics
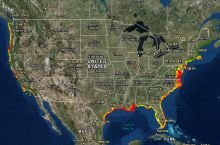
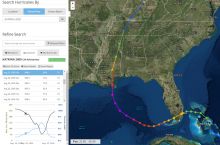
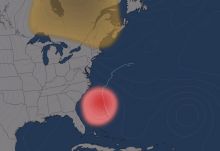
Weather hazards include hurricanes, tornadoes, thunderstorms, lightning, hail, winds, and winter weather. Many of these phenomena are related to atmospheric conditions that can be monitored and forecast. Read more
Frequently Asked Questions
Do you have a question that's not listed here? Search all FAQs
Explore Related Topics
Climate has an enormous impact on society, with wide-ranging effects on public safety and health, the economy, transportation, infrastructure, and agriculture. Geoscientists investigate our climate's past and present to better understand how it may change in the future.
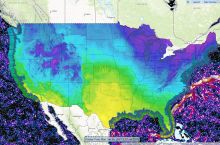
Since 1980 the United States has experienced more than 24 major droughts, resulting in almost 3,000 deaths and economic impacts exceeding $225 billion. All areas of the U.S. have some drought risk.
Flooding is the most common and costliest natural hazard facing the United States. Each year, flooding causes billions of dollars in damages and dozens of deaths nationwide.
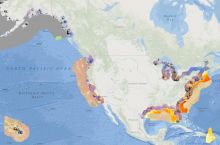
Natural hazards such as earthquakes, landslides, hurricanes, floods, and wildfires endanger public health and safety, threaten critical infrastructure, and cost our economy billions of dollars each year. Geoscientists study these hazards to provide information and warnings to populations at risk.
Landslides affect all 50 states and U.S. territories, where they cause 25 to 50 deaths and more than $1 billion in damages each year. Geoscientists study and monitor landslides to identify at-risk areas, prepare populations, and improve our understanding of why, when, and where landslides happen.
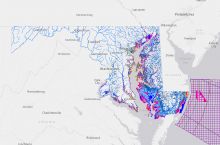
Sinkholes have both natural and artificial causes. They tend to occur most often in places where water can dissolve the bedrock (especially limestone) below the surface, causing overlying rocks to collapse. Florida, Texas, Alabama, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, and Pennsylvania are most sinkhole-prone.
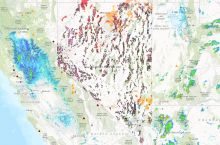
Wildfires are causing more frequent and wider-ranging societal impacts, especially as residential communities continue to expand into wildland areas. Since 2000, there have been twelve wildfires in the United States that have each caused damages exceeding $1 billion; cumulatively, these twelve wildfires have caused a total of $44 billion in damages.