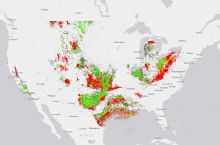
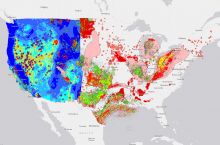
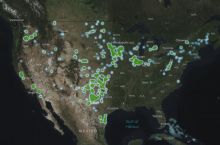
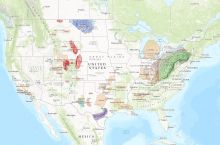
By the numbers: North Dakota
- 1,810 geoscience employees (excludes self-employed)1
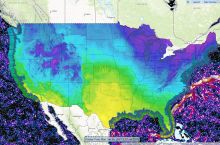
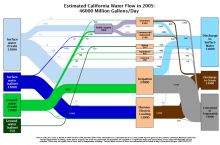
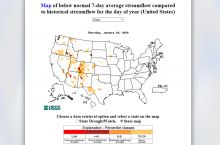
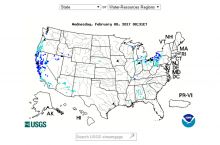
- 212 million gallons/day: total groundwater withdrawal3
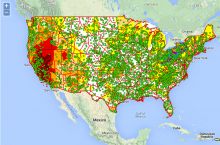
- $72 million: value of nonfuel mineral production in 20174
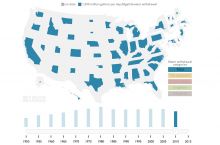
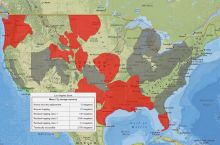
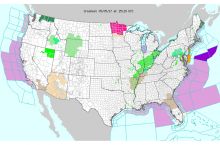
- 57 total disaster declarations, including 28 flood, 20 snow, and 3 tornado disasters (1953-2017)6
- $636,000: NSF GEO grants awarded in 201714...
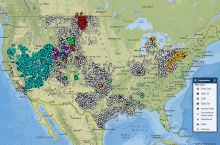
Agencies Working on Geoscience Issues in north dakota
The NDDES mission is to conduct planning, coordination, communications, and operations for the safety and security of all North Dakota citizens.
The North Dakota Department of Environmental Quality’s Vision is for a sustainable, high quality environment for current and future generations. Our Mission is to conserve and protect the quality of North Dakota’s air, land and water resources following science and the law.
In cooperation with the general public, industry and government at all levels, the department implements protective programs and standards to help maintain and improve environmental quality.
The mission of the North Dakota Department of Health is to protect and enhance the health and safety of all North Dakotans and the environment in which we live. To accomplish our mission, the North Dakota Department of Health is committed to improving the health status of the people of North Dakota, improving access to and delivery of quality health care, preserving and improving the quality of the environment, promoting a state of emergency readiness and response, and achieving strategic outcomes within available resources.
The North Dakota Department of Mineral Resources is an agency of the North Dakota Industrial Commission. The Department consists of the North Dakota Geological Survey (including its paleontology program), the Pipeline Authority (established by the state legislature in 2007 to facilitate development of pipeline facilities), and the Oil and Gas Division (which regulates the drilling and production of oil and gas in North Dakota).
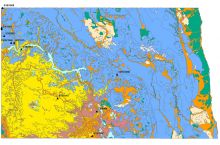
The North Dakota Geological Survey's mission is to investigate the geology of North Dakota; to administer regulatory programs and act in an advisory capacity to other state agencies; and to provide public service to the people of North Dakota.
The Public Service Commission fulfills its statutory mandates by protecting the public interest and regulating utilities, mining companies, and licensees in a fair, efficient, responsive, and cooperative manner. Regulatory initiatives assure that utility customers receive reliable and safe service at reasonable and just rates; mined coal lands are reclaimed to provide a safe and productive environment now and in the future; and license and permit holders and operators of commercial weighing and measuring devices operate in a safe and fair manner.
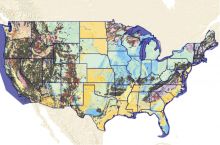
In addition to the wide variety of agencies working on geoscience issues within the North Dakota State Government, the Hub Explorer provides a large amount of information about geoscience and natural resources in the state.