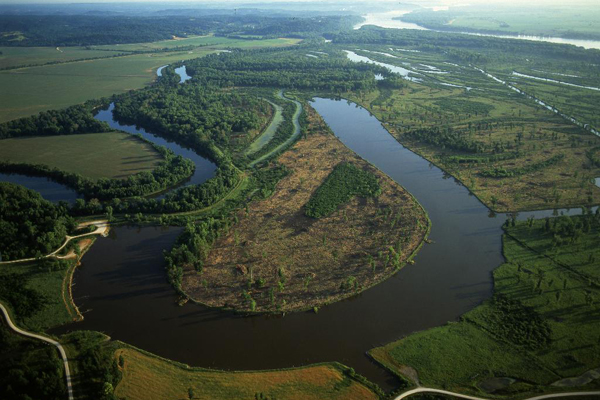
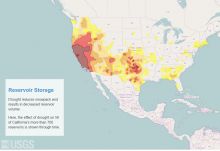
Water is constantly moving on the Earth between the atmosphere, ocean, rivers and streams, snowpacks and ice sheets, and underground. Water availability, both as surface water and groundwater, is essential for agriculture, human consumption, industry, and energy generation.
Basics
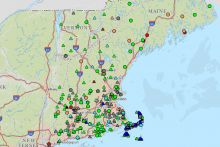
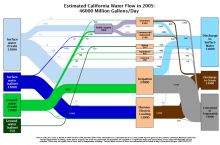
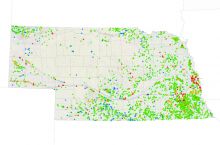
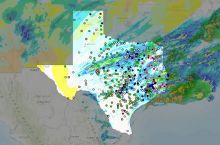
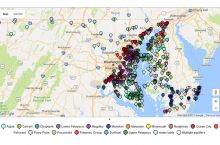
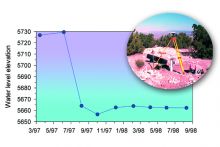
Fresh water is available as surface water (such as lakes, rivers, reservoirs) and groundwater (found underground in rock or soil layers, and accessed through wells or natural springs). Water is constantly moving on the Earth between the atmosphere, ocean, and different fresh water bodies. Climate, land use, local geology, and water quality all affect the availability of fresh water resources in addition to the direct demands people place on them. Read more
Frequently Asked Questions
Do you have a question that's not listed here? Search all FAQs
Explore Related Topics
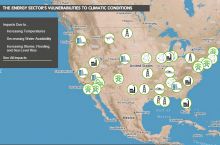
Climate has an enormous impact on society, with wide-ranging effects on public safety and health, the economy, transportation, infrastructure, and agriculture. Geoscientists investigate our climate's past and present to better understand how it may change in the future.
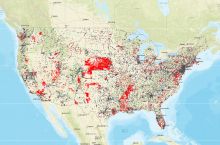
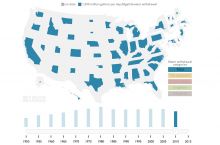
Since 1980 the United States has experienced more than 24 major droughts, resulting in almost 3,000 deaths and economic impacts exceeding $225 billion. All areas of the U.S. have some drought risk.
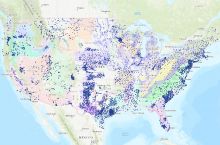
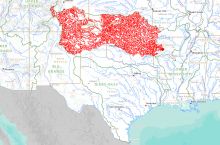
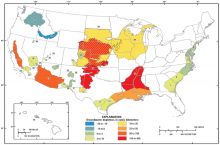
Groundwater is the water found underground in the cracks and spaces in soil, sand, and rock. Groundwater has been used by humans for thousands of years; today it provides 25% of the fresh water used in the United States, mostly for irrigation and public water supplies.
Water is essential for society and, as demand steadily rises, our most precious commodity. Geoscientists study how to provide a clean and secure water source to meet society's needs.
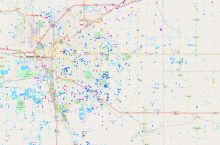
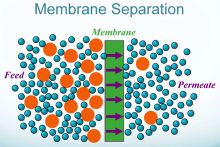
Water quality refers to whether water is suitable for a certain purpose, like drinking or irrigation. Both natural and man-made factors can affect water quality. Contaminants can include bacteria, metals, and man-made chemicals like pesticides or pharmaceutical drugs.
Wildfires are causing more frequent and wider-ranging societal impacts, especially as residential communities continue to expand into wildland areas. Since 2000, there have been twelve wildfires in the United States that have each caused damages exceeding $1 billion; cumulatively, these twelve wildfires have caused a total of $44 billion in damages.