By the numbers: Wyoming
- 2,197 geoscience employees (excludes self-employed)1
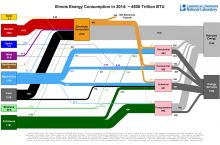
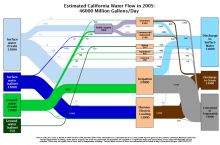
- 748 million gallons/day: total groundwater withdrawal3
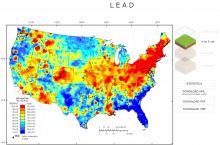
- $2.41 billion: value of nonfuel mineral production in 20174
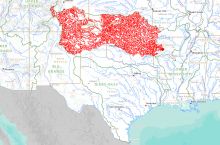
- 30 total disaster declarations, including 18 fire, 5 flood, and 2 severe storm disasters (1953-2017)⁶
- $4.65 million: NSF GEO grants awarded in 201714...
Agencies Working on Geoscience Issues in wyoming
The Wyoming Department of Environmental Quality is responsible for enforcing state and federal environmental laws. It is comprised of seven divisions inluding: administration, abandoned mine land, air quality, industrial siting, land quality, solid & hazardous waste, water quality.
Among the SERC's duties are the following: designate local emergency planning districts within the state and appoint a local emergency planning committee (LEPC) to serve each of the districts; coordinate and supervise activities of the local committees; review local emergency response plans annually; receive all chemical release notifications and inventory reports.
The Wyoming State Geological Survey (WSGS) performs the important and critical function of interpreting Wyoming’s complex geology.