By the numbers: Texas
- 54,266 geoscience employees (excludes self-employed)1
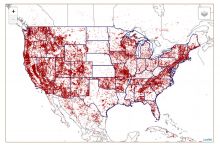
- 7.2 billion gallons/day: total groundwater withdrawal3
- $5.22 billion: value of nonfuel mineral production in 20174
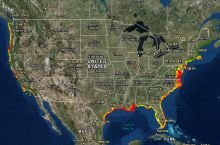
- 254 total disaster declarations, including 154 fire, 36 flood, and 20 hurricane disasters (1953-2017)⁶
- $70.2 million: NSF GEO grants awarded in 201714...
Agencies Working on Geoscience Issues in texas
In addition to functioning as the State Geological Survey of Texas, the Bureau of Economic Geology in the Jackson School of Geosciences conducts research focusing on the intersection of energy, the environment, and the economy, where significant advances are being made tackling tough problems globally. The Bureau partners with federal, state, and local agencies, academic institutions, industry, nonprofit organizations, and foundations to conduct high-quality research and disseminate the results to the scientific and engineering communities as well as to the broad public.
The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality strives to protect the state's public health and natural resources consistent with sustainable economic development. Our goal is clean air, clean water, and the safe management of waste.
The Texas Division of Emergency Management (TDEM) coordinates the state emergency management program, which is intended to ensure the state and its local governments respond to and recover from emergencies and disasters, and implement plans and programs to help prevent or lessen the impact of emergencies and disasters.
The Texas State Soil and Water Conservation Board (TSSWCB) is the state agency that administers Texas’ soil and water conservation law and coordinates conservation and nonpoint source water pollution abatement programs throughout the State.
The mission of the Texas Water Development Board (TWDB) is to provide leadership, information, education, and support for planning, financial assistance, and outreach for the conservation and responsible development of water for Texas.